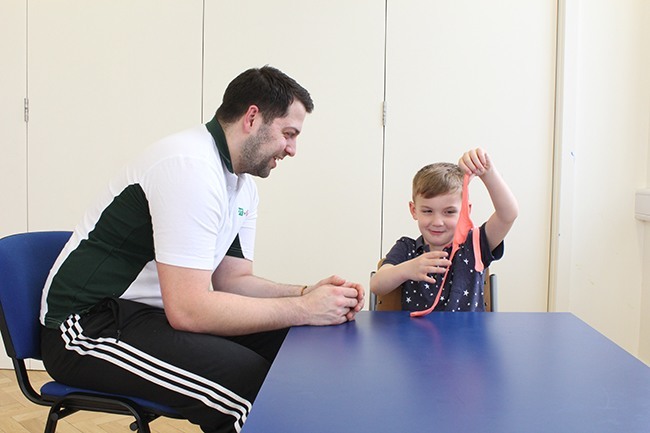
Fine Motor Improvement Therapy
Fine motor activities are the games and tasks we complete that require the use of our hands. These involve handwriting, doing up buttons, picking up small objects, manipulating items in hand, changing the channel and many more tasks. It is vitally important that children get lots of practice with fine motor activities and games. The most common household items can be used to promote hand skills, for example cutting up a sponge into small squares dipping them in paint and creating artwork, or by using toothpicks and grapes to create 2D and 3D shapes is a great way to practice fine motor skills. Useful board games for developing fine motor control include games similar to pop-up pirate, Jenga or chess.
What are fine motor skills?
Fine motor skills are essentially the ability to manipulate objects with the hands. However, this is not a simple task, involving a variety of intricate and well-timed movements of the hand. Aspects of fine motor skills are:
| Fine motor skill | Definition | Task Need |
| In hand manipulation | The ability to manipulate objects using the palm and fingers of one hand | Manipulating coins Building blocks |
| Finger strength and control | The ability to apply the correct level of pressure when holding objects | Grasping and stabilising objects Drawing/writing |
| Finger isolation | The ability to use one finger at a time whilst maintaining control of the other fingers | Finger painting Musical Instruments |
| Pincer grasps | The grasp used to maintain control whilst trying to place one object through another | Pencil control Threading Coin slots |
| Thumb opposition | The ability to turn and rotate the thumb to touch each finger of the hand | Grasp objects varying in size Use tools (bat, toy gun etc) |
| Bilateral coordination | The ability to coordinate hand movements using both hands at the same time to manipulate objects | Tying shoe laces Unscrewing tops/pulling lids |
| Crossing the midline | The ability to cross one hand from one side of the body to the other | Drawing large pictures Threading |
| Eye-hand coordination | The ability to use sight to guide the movements of the hand | Every task involving the hands |
| Posture | The ability to use the core and upper body to stabilise the arms and hands | Writing Threading |
| Pencil control | The ability to apply correct amounts of pressure and direction when holding a pencil | Writing Drawing |
| Visual perception | The ability to perceive and control the movements of the hand | Writing Threading Every other Fine motor task |
| Sensory integration | The ability to process the sensory feedback from objects (feel, pressure, hot, cold) | Every task Writing Threading Buttons out of sight |
The purpose of fine motor skills during childhood are to enable children to complete important school and home based occupations such as writing, threading, dressing and tying shoe laces. Without the ability to complete these activities children will be left behind academically compared to class mates, especially with handwriting. These early development of fine motor skills are honed and improved over time and into adulthood to ensure that they are a high functioning independent adult.
Problems that may require fine motor improvement therapy
Below is a list of common problems associated with fine motor control, that an occupational therapist can help improve.
- Unable to tie shoes
- Poor handwriting
- Difficulty getting dressed
- Inability to do up buttons
- Slow at fine motor games
- Struggles to manipulate objects with both hands
- Often compensating by using the body to stabilise objects
- Struggles to undo sandwich wrappers/lunch box
Suitable conditions
Below is a list of conditions that are commonly found alongside fine motor control difficulties, this is not an exclusive list.
- Dyspraxia
- Cerebral Palsy
- Acquired head injury
- Developmental Delay
- Developmental Co-ordination disorder
- Muscular Dystrophy
- Stroke
- Sensory Processing Disorder
The occupational therapists has the relevant skills, knowledge and observation skills to pinpoint the difficulties your child is having and explain why they may be experiencing these and offer effective treatment sessions that can improve these skills. To be referred for an Occupational Therapy assessment or to discuss anything in more detail please email office@otforkids.co.uk or call us on 0330 223 0888

 Next steps:
Next steps:Please contact one of our experienced occupational therapists today and we will gladly discuss how we can help and what services we can offer you.
- 0330 223 0888
- office@otforkids.co.uk
- 2 Hagley Rd, Salford M5 3EY [map]







 OT for Kids have been a great help in aiding my son Jake with coping with his dyspraxia both at home and in school. They came out to our house and completed the assessment at home.
OT for Kids have been a great help in aiding my son Jake with coping with his dyspraxia both at home and in school. They came out to our house and completed the assessment at home.