Gross Motor Activity Training
Gross motor activity training is a type of treatment aimed at improving the perception, balance, hand eye co-ordination and many other aspects that are termed under the umbrella of gross motor function. The occupational therapist would use a variety of games and activities to improve movement.
What does gross motor mean?
Gross motor literally translates too large movements, or movements that require a large proportion of the body to move (such as legs, arms and trunk when running). Gross motor movements are the main skills we need to move on a daily basis, or more specifically move safely and successfully in space.
Why do we need gross motor activities?
Controlled movements allow us to run, hop, jump, bend, skip, and do physical activities such as star jumps and sit ups etc effectively. Only through these movements being performed correctly can we successfully compete in sport, complete physical education lessons, safely move around at home/school without bumping into things, or play with other children outside safely.
What are gross motor activities?
Gross motor activities vary greatly in complexity, however there are fundamental underlying skills that support and enable all of us to complete these complex activities. The term gross motor can be broken down into a series of terms used to describe the subconscious thoughts we all use every time we run/hop/jump/skip and complete other similar activities. Below is an inconclusive list of these aspects:
- Balance
- Posture
- Hand/foot-eye co-ordination
- Visual and auditory figure-ground discrimination
- The ability to distinguish depth of a sound/object in space
- Proprioception
- The perception of their body/limbs in space
- Bilateral integration and co-ordination
- The use and control of both hands/feet in relation to objects in space
- Spatial Awareness
- Assess and move accordingly to spatial relationships between objects and the body
- Floor based activities
- Sit ups, four point balancing, push ups, rolling over
- Initiate movements
- Start movements on command
- Stabilising muscle movements
- Needed for balance when bending
- Stop movements on command without overflow
- Stop movements immediately without carrying after stop command
- Rhythmicity of movement
- Move in a similar pattern to music/rhythm
- Motor planning and timing
- Plan and time movements successfully in relation to the task
- Motor execution
- The ability to control and execute smooth movements independently
- Midline Orientation
- Bringing the hands to the middle of the body
- Temporal awareness
- Appreciation of speed and timing
- Form consistency
- Appreciation of the size of objects
- Vestibular regulation
- Balance regulation using the receptors in the inner ear
- Maintain balance in sitting, standing and moving
- Detecting speed and direction of movements
- Memorising and recalling muscle movement patterns (Muscle memory)
- Complete memorised motor patterns
- Learn and remember new motor patterns
- Listening, understanding and responding to instruction
Problems that may require gross motor activity training
Some of the problems that may require gross motor activity training include:
- Poor balance
- Clumsy
- Poor Physical Education grade
- Slow at completing movements
- Difficulty co-ordinating more than one movement at the same time
- Messy eater
- Difficulty riding bike/pedalling
- Poor swimmer
Top down therapy analyses the task and through therapy, the task is repeated, simplified and made more difficult until the child has developed the skills needed to complete this particular task. As a consequence the underling skills will also improve, but only in relation to this one particular task.
However, bottom up therapy takes a more foundational approach, it focuses on improving the skills underlying the task (such as balance, core strength and hand eye co-ordination), with the aim of improving the overall task speed and success through improvement in these foundation skills. These improved foundation skills can be transferable across other tasks (not just the highlighted task).
Conditions that require gross motor training:
Conditions can have a further burden on a child's development, below is a list of conditions that impact on function:
- DCD
- Dyspraxia
- Cerebral Palsy
- Stroke
- Acquired brain/head injury or trauma
- Developmental delay
- Muscular Dystrophy
- Sensory Processing Disorder
Benefits of gross motor activity training:
- Improved balance
- Improved co-ordination
- Better performance in sport P.E and swimming
- Able to play and compete on a similar level to classmates
- Improved confidence in independence and ability
- Improved perception skills
- Muscle strengthening
- Improved instruction attention and understanding
- Motor planning and execution optimisation
- Improved proprioception skills
Summary
In summary gross motor activity training will improve your child's gross motor skills. Gross motor literally translates too large movements, or movements that require a large proportion of the body to move. Problems that may require gross motor activity training include poor balance, clumsiness and slow uncoordinated movements. If you think your child is struggling in P.E or tends to bump into things often then please email office@otforkids.co.uk or call us on 0330 223 0888
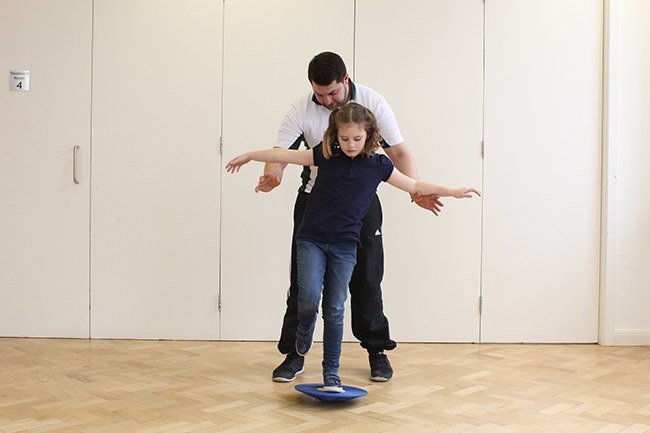

 Next steps:
Next steps:Please contact one of our experienced occupational therapists today and we will gladly discuss how we can help and what services we can offer you.
- 0330 223 0888
- office@otforkids.co.uk
- 2 Hagley Rd, Salford M5 3EY [map]







 OT for Kids have been a great help in aiding my son Jake with coping with his dyspraxia both at home and in school. They came out to our house and completed the assessment at home.
OT for Kids have been a great help in aiding my son Jake with coping with his dyspraxia both at home and in school. They came out to our house and completed the assessment at home.